The Nervous System
The nervous system is a complex network that coordinates every action and response in the body, from voluntary movements to automatic processes. It is divided into the central nervous system (CNS), the brain and spinal cord, which processes information, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), which transmits signals between the CNS and the rest of the body. Together, they regulate everything from thought and memory to breathing, digestion, and reflexes, ensuring the body maintains balance and adapts to internal and external changes.
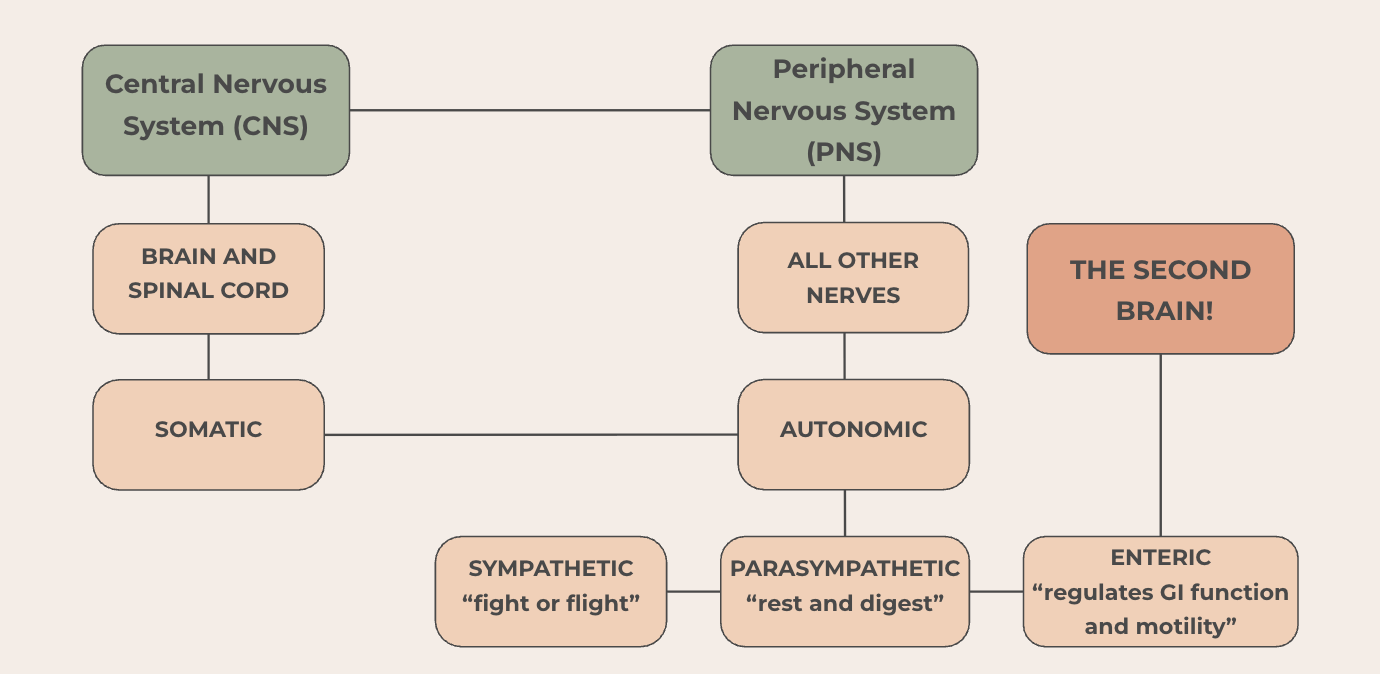
Sympathetic
Known as the “rest and digest” system, it calms the body after stress by lowering heart rate, promoting digestion, and restoring energy levels. It helps maintain homeostasis during relaxed states.
Parasympathetic
Often called the “fight or flight” system, it activates during stress or danger by increasing heart rate, redirecting blood flow to muscles, and releasing adrenaline to prepare the body for quick action.
Enteric
Referred to as the “second brain,” this system is embedded in the gastrointestinal tract and independently controls digestion. It communicates with the brain via the gut-brain axis, influencing mood, immunity, and overall health.

